Simple Design of Communication Service
Few months back, I had to make some changes to design of Communication Service.
It was quite a complex architecture overall and I thought of documenting this in blogpost to outline my thought process.
A communication service is responsible for reliably delivering the customer notification to the end user via any channel.
In our case, the channels were email, SMS and push notification.
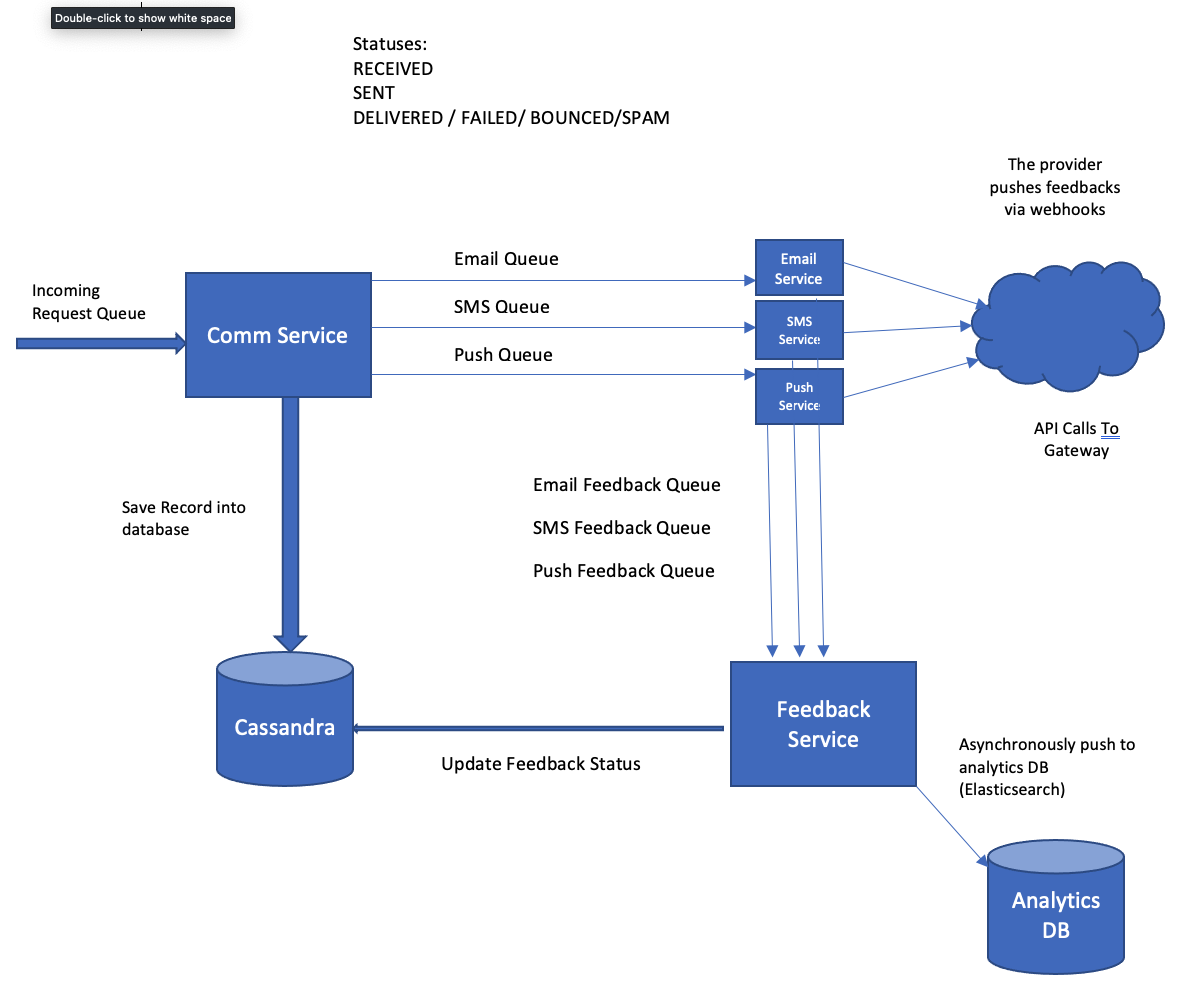
The communication service was divided into multiple microservices:
Communication Services
This was the main service which recieved payloads from other microservices whenever they had to send out a communication.
The payload was json and interaction was via kafka queue.
Key points: We had to make sure we monitor the kafka queue for lag very closely. As any lag can potentially delay the communication to the end user.
The communication service did the enrichment to the payload such as creating the email template, SMS template from its template database and pushed the enriched payload to individiual channel kafka queues. We wanted to have individual channel queues for independently scaling them. For instance, our traffic on email was much higher compared to SMS and push notification. That way, we could scale the partitions on email kafka and queue.
The communication service also generates a unique uuid for each request and persists into cassandra database. This serves as a single point of lookup for
Email / SMS / Push Service
These are individual micro services listening to each of the channel queues. They make a rest call to the provider to actually deliver the email. Once the rest call is successfully made, we push the status message on a feedback kafka queue dedicated for each channel.The feedback kafka queues are again channel independent to allow them to independently scale.
These services also contain webhook listeners. Typically, when you delivery a email / SMS / push via a vendor, vendor will send the feedback via webhook weather the mail / SMS / push was successfully delivered, or if it bounced or if it went to spam etc.
It is important to have circuit breaker in these services as vendor services might go down any moment. Thus, it is important to have a dead letter queue, which would retry the failed pushes later.
These feedbacks are also sent to the same feedback queues as updates.
We could have had a separate service for feedback altogether, but I believe it didn’t require a separate microservice altogether which would expanded our monitoring footprint.
Feedback Service
This is the main services which receives all the updates w.r.t. each communication. These updates are consumed via feedback queues. It is important to scale this service sufficiently as we didn’t had a separate feedback service for each channel in order to have lesser complexity. Our email feedback kakfa topic had 200 partitions and there were 20 computes each running 10 threads to consume from these partitions.
The job of the feedback service is to receive the feedback and push it to cassandra database. It asynchronously also pushes the feedback to analytics channel mainly an elasticsearch database for analytics purpose, since cassandra is not suited for doing analytics.
The final design looked like this: